How to read the diagrams
An aquascape is a diagram generated from a stream program.
Aquascapes can be used to illustrate the behaviour of fs2 operators. By reading the diagrams, you will learn more about the operators and streams.
This page describes:
- The stage model that underpins aquascapes.
- How to read basic aquascapes.
- How to read aquascapes with effects and errors.
- A summary of all the symbols used in aquascapes.
The stage model
A stream is built from stages. When evaluated:
- Each stage pulls on the stage above.
- It outputs an element to the stage below.
- If there are no more elements to output, the stage is done.
- It might also evaluate an effect.
- That effect might raise an error.
Basics
This code snippet:
Stream('a', 'b', 'c')
.take(2)
.compile.toListcorresponds to the following diagram:
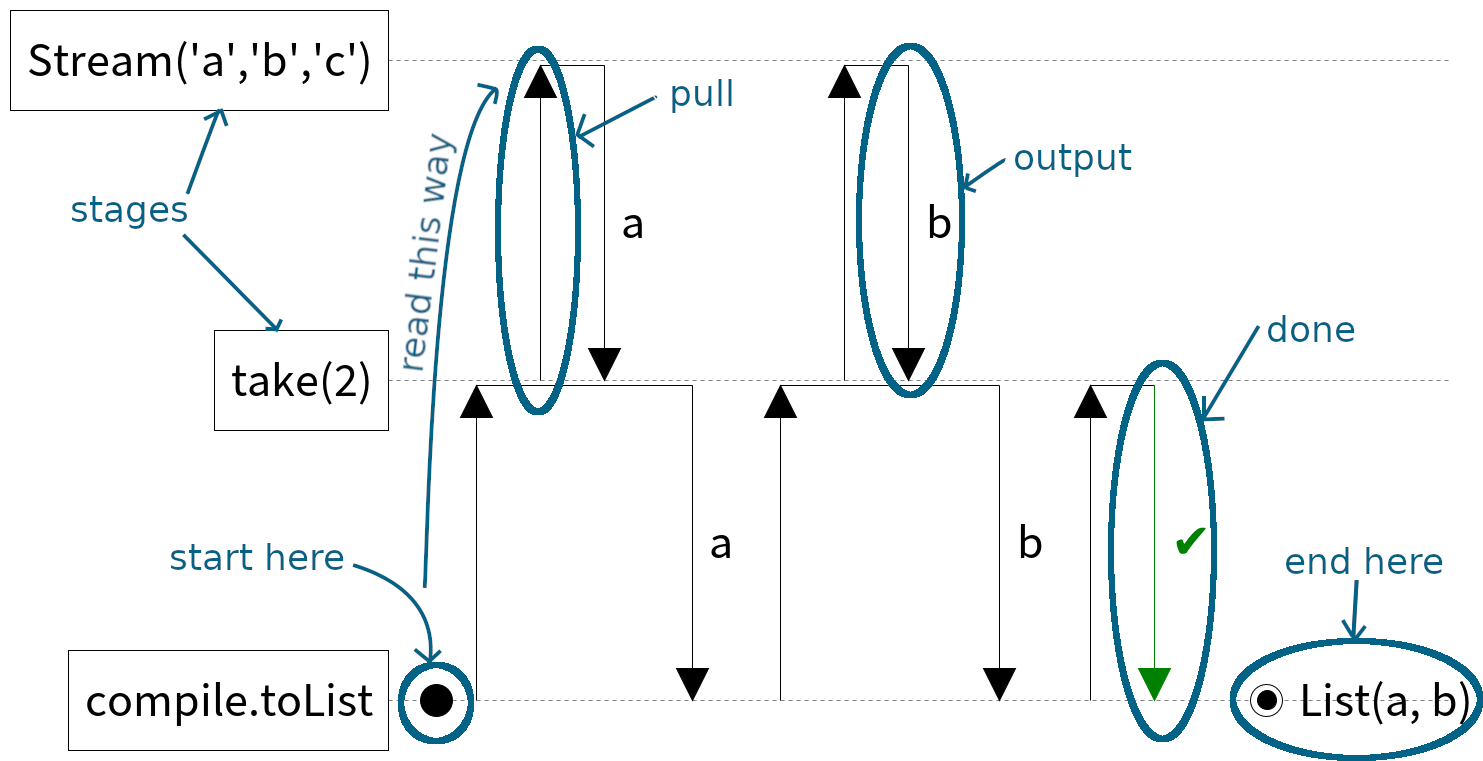
Effects and errors
Aquascapes can also show the result of evaluating effects. If the effect raises in an error, that error is also shown.
Stream('a', 'b', 'c')
.evalMap(x => IO.raiseWhen(x == 'b')(Err))
.compile.toList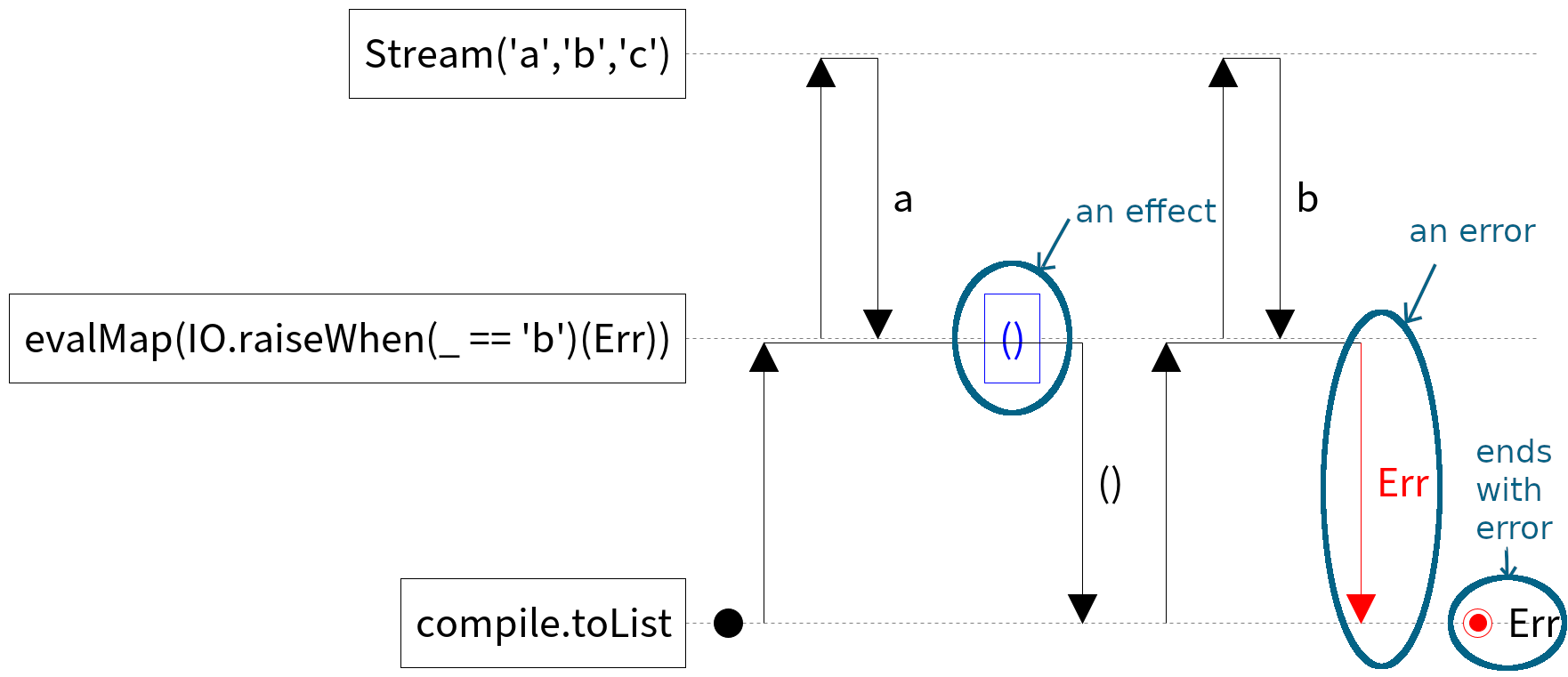
Symbol guide
This section describes the different symbols used in an aquascape.
Start
A black dot corresponds to the start of the program. Start reading the diagram from here and follow the arrows upwards.
End
A black dot with a rim corresponds to the end of the stream program. The text next to the dot is a string representation of the resulting value. In this example, running the stream results in the value Some(a). A possible program that results in this is Stream('a').compile.last.
End with error
A red dot with a rim and red text indicates that the stream program terminated with an error. The text next to the dot is a string representation of the error.
Stage
A box on the left hand side of the diagram is a stage of the stream. A stream is composed of several stages. For basic streams, each stage will correspond to an operator in the code snippet that generates the diagram. For example, take(2) may be a stage in Stream('a').take(2).compile.toList.
Pull
An arrow up represents a pull from one stage to another. A pull always has a corresponding arrow downwards for its result.
Results of a pull
A downwards arrow is the result of a pull. A result can be an output, an error, or done.
Output
An arrow down with text next to it represents an outputted value. The text is a string representation of the value. For example, the text in this arrow indicates that the character 'a' was outputted.
Chunks
If the output is surrounded by square braces, it represents a chunk of values. Most diagrams are simplified to display individual values. Diagrams that display chunks show the actual pull and output semantics of a stream.
Error
An arrow down with red text next to it corresponds to an error. The text is a string representation of the error.
Done
An arrow down with a green check mark next to it indicates that the stage is done. The stage cannot output any more elements.
Evaluation
A blue box containing text represents the evaluation of an effect. The text is a string representation of the result of the effect. For example a indicates that the effect outputted the character 'a'. The effect might have been IO('a').
Time
A purple circle with a number of seconds within it corresponds to the passage of time. In this example, one second passes.